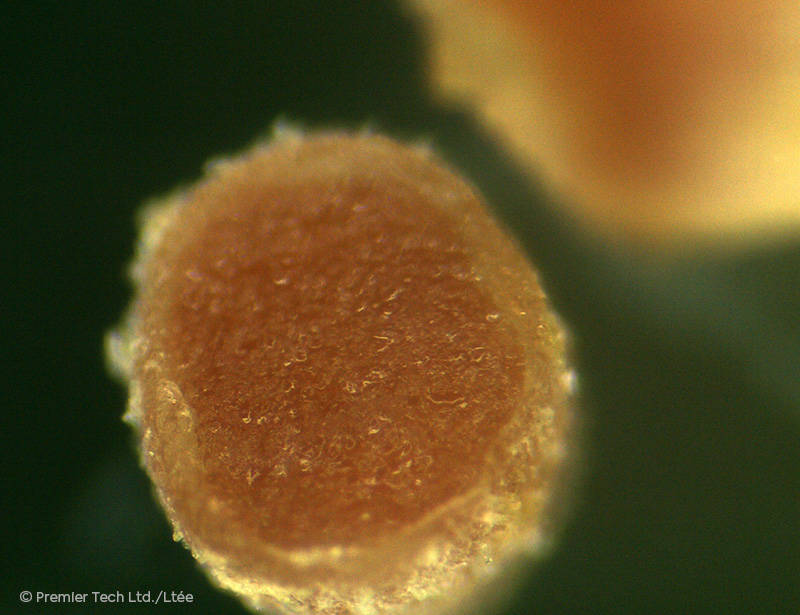
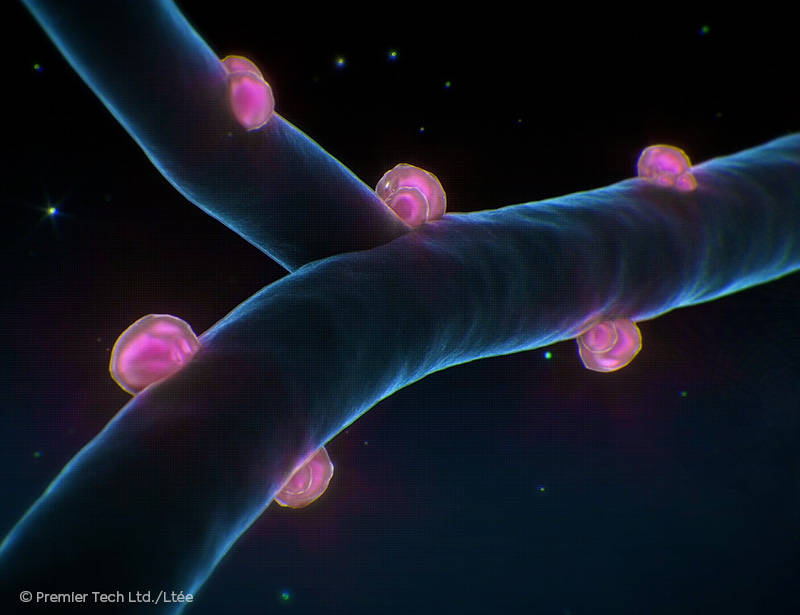
AGTIV FUEL® feeds legumes by fixing atmospheric nitrogen thanks to rhizobium.
 Rhizobium
Rhizobium
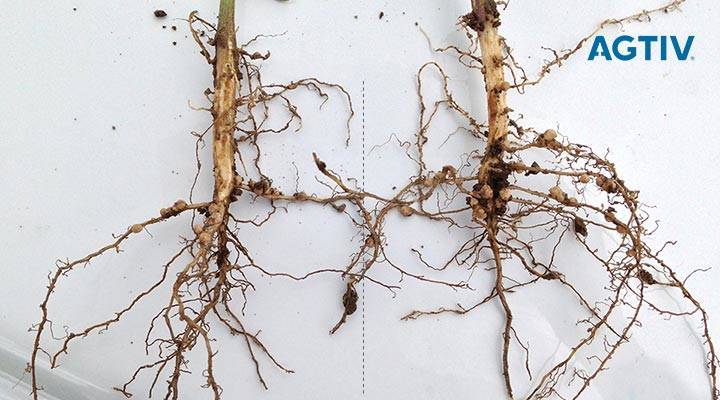
- Increases nodulation
- Fixes nitrogen
- Provides nutrients to pulses
How Rhizobium Work
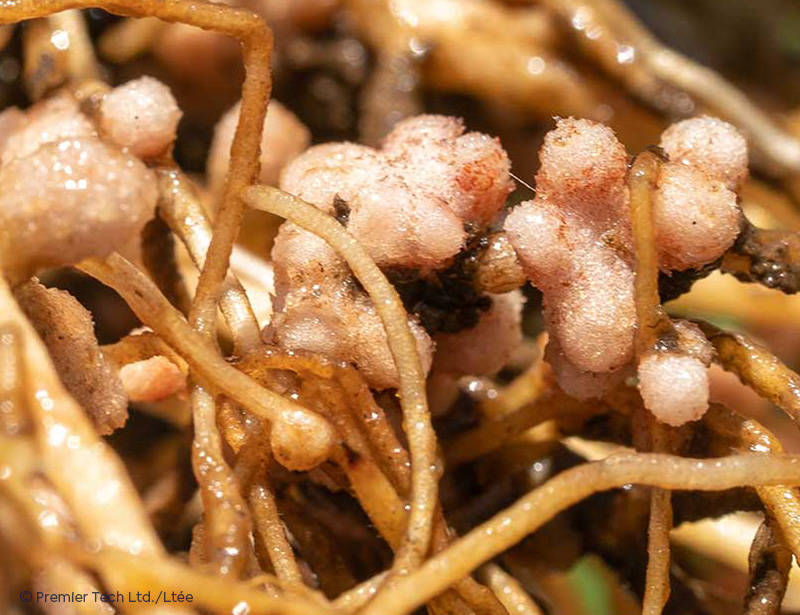
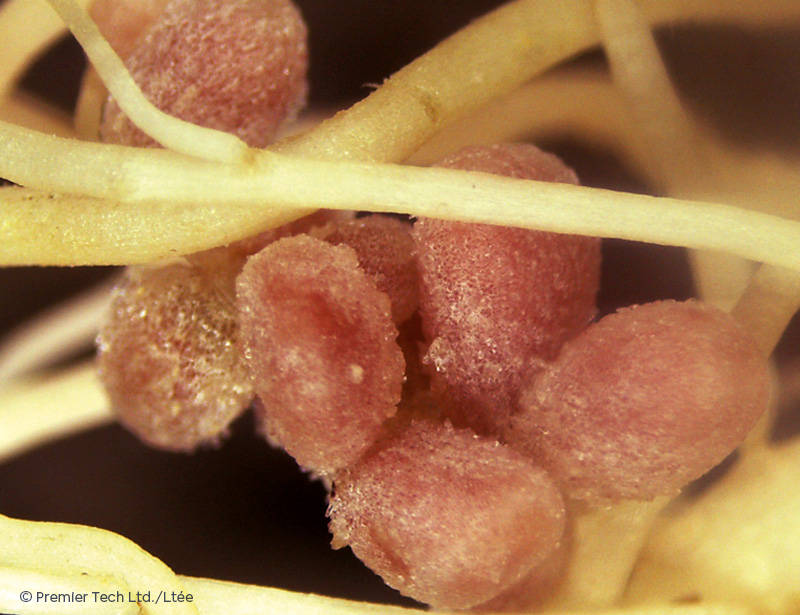
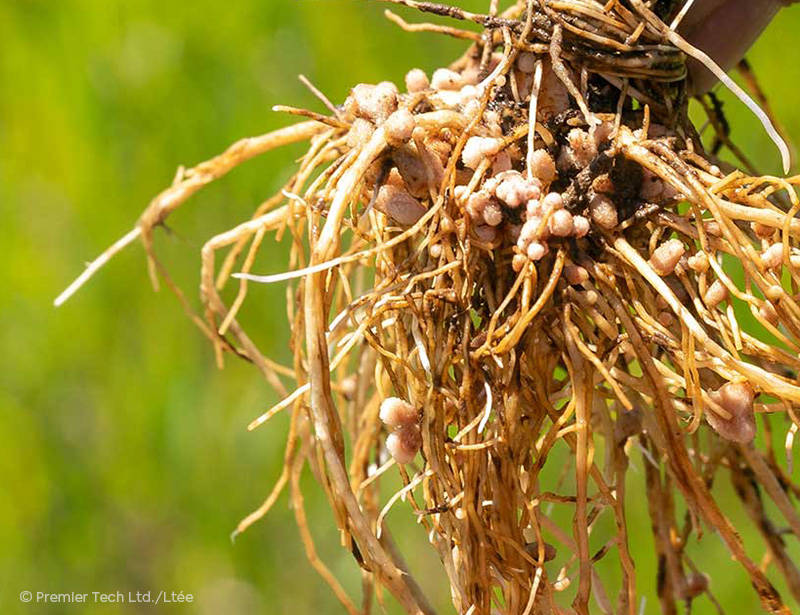
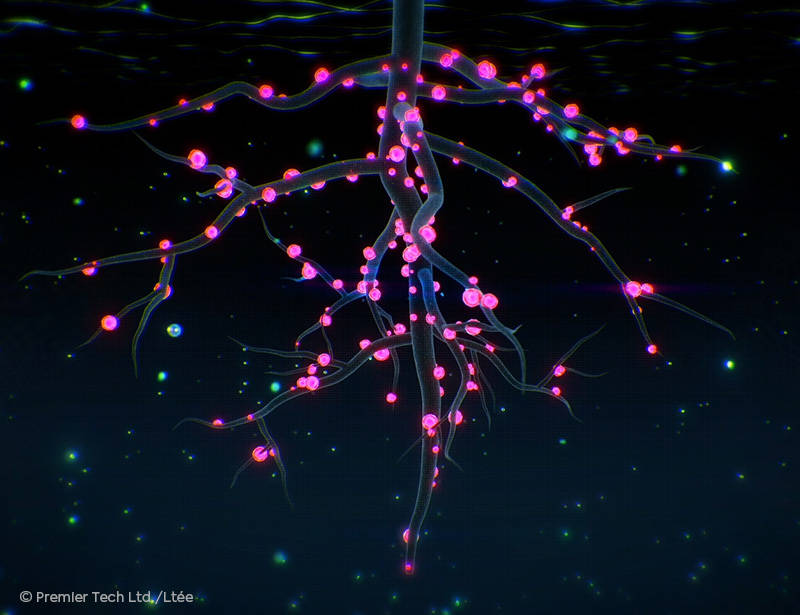
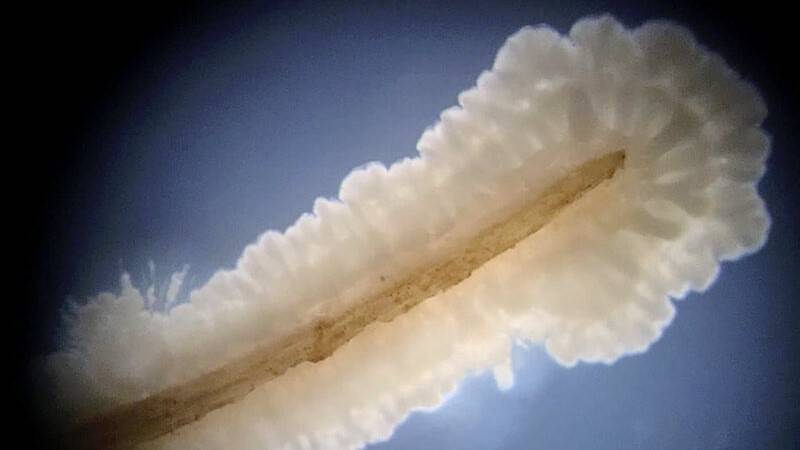
Nodule Formation
When beneficial rhizobium bacteria are near a plant, they emit signals called "nodulation factors", which are picked up by the root hairs and lead to the formation of nodules.
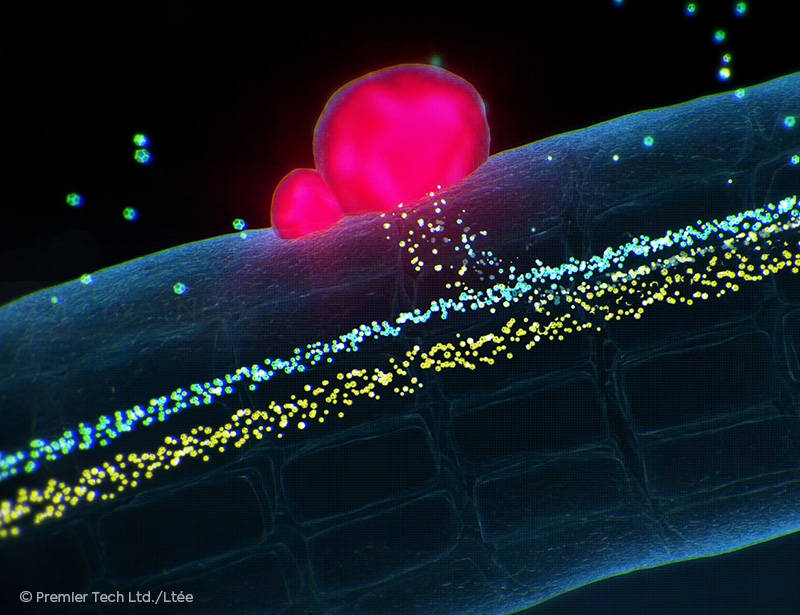
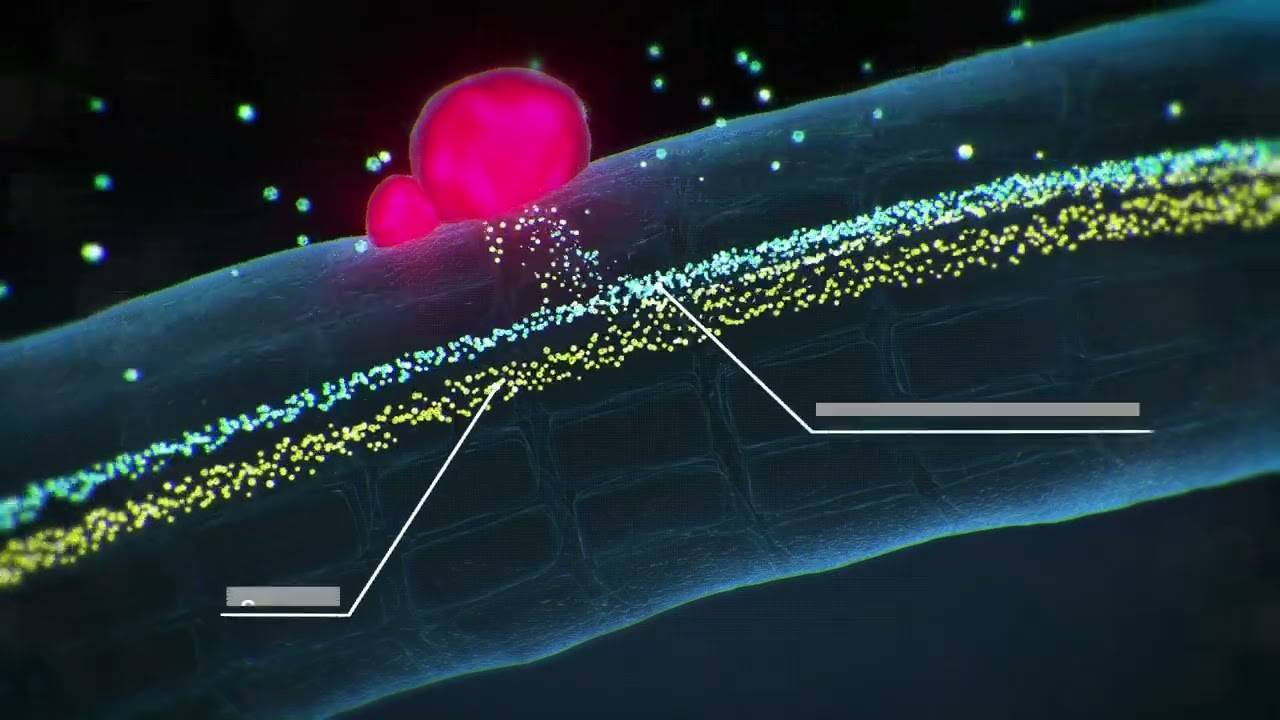
Nitrogen Production and Transfer
In this mutually beneficial relationship, rhizobium bacteria utilize nodules to fix the atmospheric nitrogen required for legume growth.
Plant-Rhizobium Mutual Exchange
Nodules act as factories for the production and transfer of nitrogen in a form the plant can use for protein production. In exchange, the plant supplies phosphorus and sugars to the rhizobium.
Key Benefits of Rhizobium for Crops
Curious to see how AGTIV FUEL® can make a difference in your crops? This technology enhances nodulation, nitrogen fixation, and plant nutrition while improving root environment, vigor, and overall performance. Experience larger leaves, accelerated row closure, and fuller pods, empowering your crops for optimal growth and yield. For you, this means improving crop productivity and profitability with ease.
Gallery